Design and synthesis of enzyme inhibitors
Our research involves the development of enzyme inhibitors. For example, histone deacetylases catalyse the removal of acetyl groups from the terminally acetylated lysine residues on histones This leads to a compacted (chromatin) structure in which regions of DNA have become inaccessible for transcription. Such gene repression can be associated with cancer, and HDAC inhibitors are considered an important anti-cancer therapy, but have also been proposed for use in several other diseases including Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases.
Selected publications
A Direct Alkylation Route to Branched Derivatives of Suberolylanilide Hydroxamic Acid (SAHA), a Potent Non-selective Inhibitor of Histone Deacetylases
Dines, J.A., Marson, C.M.
Tetrahedron (2016) 72 (52):8584-8592
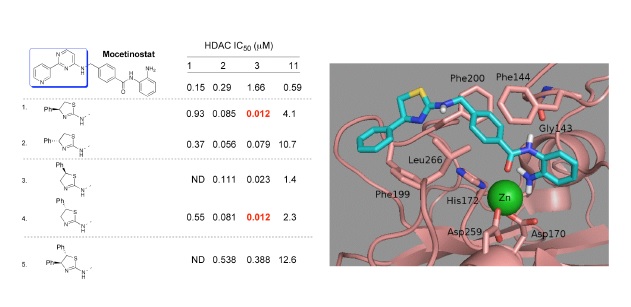
Discovery of Potent, Isoform-Selective Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase containing Chiral Heterocyclic Capping Groups and a N-(2-Aminophenyl)-benzamide Binding Unit
Marson, C.M., Matthews, C.J., Yiannaki, E., Atkinson, S.J., Soden, P.E., Shukla, L., Lamadema, N., Thomas, N.S.B.
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2013) 56(15):6156-6174
Potent, and Selective Inhibitors of Histone Deacetylase-3 containing Chiral Oxazoline Capping Groups and a N-(2-Aminophenyl)-benzamide Binding Unit.
Marson, C.M., Matthews, C.J., Yiannaki, E., Atkinson, S.J., Lamadema, N., Thomas, N.S.B.
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2015) 58 (17):6803-6818